In times of high availability and multiple web servers, central data storage, data security and fast access times must be harmonized. This is precisely why more and more users are now using technologies that lure them in with buzzwords such as S3, buckets, object storage and Swift. We at NETWAYS Web Services have been offering this for some time now. We have created this tutorial to shed some light on the subject. In this tutorial we will explain it step by step:
- Why Objectstorage
- Creation of S3 credentials via OpenStack API
- Configuration of s3cmd
- Creating a new bucket
- Store files in the bucket
- List bucket contents
- Download file from bucket
- Further s3cmd application examples
- Concluding
Why Objectstorage?
S3 object storage offers many advantages over locally stored data or classic NFS storage, as an NFS setup often only consists of a single server and therefore represents the single point of failure. The administrator must also always be concerned about the performance of the storage and the web servers used.
Another advantage of object storage is the size and number of data to be stored. This is because, in the case of object storage, there is no limit. The provider of the object storage (in this case NWS) ensures that space never runs out. With your own NFS, the size must be taken into account in the planning from the outset and the customer pays for the planned reserve in the long term. With object storage, only the volume that is used is paid for. It is also worth mentioning the reduction in load on the web server, especially with regard to locally stored data.
Imagine the following architecture: The application is operated on several web servers, images and other objects are stored in object storage and delivered directly to the website visitor through intelligent integration, without burdening your own web servers or their bandwidth. In short, you tell your application not to deliver this specific image, but instead the application only passes on the path of the stored image to the visitor. The image is ultimately delivered directly by the underlying Rados gateway and was never delivered by the app server.
This means that it reaches the website visitor quickly, saves bandwidth and reduces the load on your own web server, while still being kept centrally. Incidentally, Objectstorage uses our Ceph, where all data is distributed across a large number of systems and naturally also has corresponding replica sets.
Creation of S3 credentials via OpenStack API
A cloud account is required to be able to use object storage with NWS. It is important to note that the credentials for S3 should be created using the OpenStack Project User Account. Once this is ready, you can get started. In OpenStack, go to the menu item “API access” and download the OpenStack RC file (top right). The script that has just been downloaded is now started on the local machine. Only the OpenStack password is requested. But beware, an OpenStack client is required.
source 9231-openstack-4707c-openrc.sh
Please enter your OpenStack Password for project 9231-openstack-4707c as user 9231-openstack-4707c:Now the EC2 credentials for S3 access need to be created using the command:
openstack ec2 credentials createThe result provides an output similar to the following:
+------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| access | aceab8b6b85c51f8d3b305aec1af39c2 |
| links | {'self': 'https://cloud.netways.de:5000/v3/users/24c527b4929f10bd6c6ee09af4b30be2/credentials/OS-EC2/aceab8b6b85c51f8d3b305aec1af39c2'} |
| project_id | a40c737aaf3027d87e98f309f9f671d4 |
| secret | e5d312a7627cdf2a87ac4322a6d7716b |
| trust_id | None |
| user_id | 24c527b4929f10bd6c6ee09af4b30be2 |
+------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+Configuration of s3cmd
s3cmd is now configured for further use. This requires s3cmd to be installed. The setup starts with s3cmd --configure
In the following wizard, the previously created data is entered, which then looks something like this (relevant entries in bold).
s3cmd --configure
Enter new values or accept defaults in brackets with Enter.
Refer to the user manual for a detailed description of all options.
Access key and Secret key are your identifiers for Amazon S3. Leave them empty for using the env variables.
Access Key: aceab8b6b85c51f8d3b305aec1af39c2
Secret Key: e5d312a7627cdf2a87ac4322a6d7716b
Default Region [US]:
Use "s3.amazonaws.com" for S3 Endpoint and not modify it to the target Amazon S3.
S3 Endpoint [s3.amazonaws.com]: rgw1.netways.de
Use "%(bucket)s.s3.amazonaws.com" to the target Amazon S3. "%(bucket)s" and "%(location)s" vars can be used
if the target S3 system supports dns based buckets.
DNS-style bucket+hostname:port template for accessing a bucket [%(bucket)s.s3.amazonaws.com]: rgw1.netways.de/%(bucket)s
Encryption password is used to protect your files from reading
by unauthorized persons while in transfer to S3
Encryption password:
Path to GPG program:
When using secure HTTPS protocol all communication with Amazon S3
servers is protected from 3rd party eavesdropping. This method is
slower than plain HTTP, and can only be proxied with Python 2.7 or newer
Use HTTPS protocol [Yes]:
On some networks all internet access must go through a HTTP proxy.
Try setting it here if you can't connect to S3 directly
HTTP Proxy server name:
New settings:
Access Key: aceab8b6b85c51f8d3b305aec1af39c2
Secret Key: e5d312a7627cdf2a87ac4322a6d7716b
Default Region: US
S3 Endpoint: rgw1.netways.de
DNS-style bucket+hostname:port template for accessing a bucket: rgw1.netways.de/%(bucket)s
Encryption password:
Path to GPG program: None
Use HTTPS protocol: True
HTTP Proxy server name:
HTTP Proxy server port: 0
Test access with supplied credentials? [Y/n] n
Save settings? [y/N] y
Configuration saved to '/Users/gmimietz/.s3cfg'In order for the S3 commands to work as desired, a small adjustment must be made to the config that has just been created.
vim ~/.s3cfgThere the line
signature_v2 = Falseadapted to:
signature_v2 = TrueOnce you have saved, you can start using it.
Creating a new bucket
A new bucket is created using the following command:
s3cmd mb s3://myfirstbucketTo check the creation of the bucket, it is listed using :
s3cmd lsStore files in the bucket
Time to upload the first files. The put parameter is used for this.
s3cmd put /Users/gmimietz/Downloads/water.liquid s3://myfirstbucket/List bucket contents
To see what is in the bucket that has just been filled, the ls command lists the contents. However, this is now supplemented by the bucket name
s3cmd ls s3://myfirstbucket
2021-02-02 11:04 402088862 s3://myfirstbucket/water.liquidDownload file from bucket
The file that has just been uploaded can now be downloaded using the get parameter.
s3cmd get s3://myfirstbucket/water.liquidFurther s3cmd application examples
Here are some helpful commands: Move an object from one bucket to another:
s3cmd mv s3://myfirstbucket/water.liquid s3://mysecondbucketStore an object encrypted in the bucket (requires a predefined passphrase (s3cmd --configure).
s3cmd put fire.element s3://myfirstbucket -eA very valuable command is the sync to synchronize a local directory with a bucket (everything below /important-data is synced to s3://myfirstbucket/backup/ ).
s3cmd sync /important-data/ s3://myfirstbucket/backup/To conserve bandwidth in certain applications, the --limit-rate option helps. This is specified as bytes by default, but the option also recognizes a k or m suffix (kilo/megabyte) per second.
s3cmd put myfile s3://myfirstbucket --limit-rate=1kConclusion
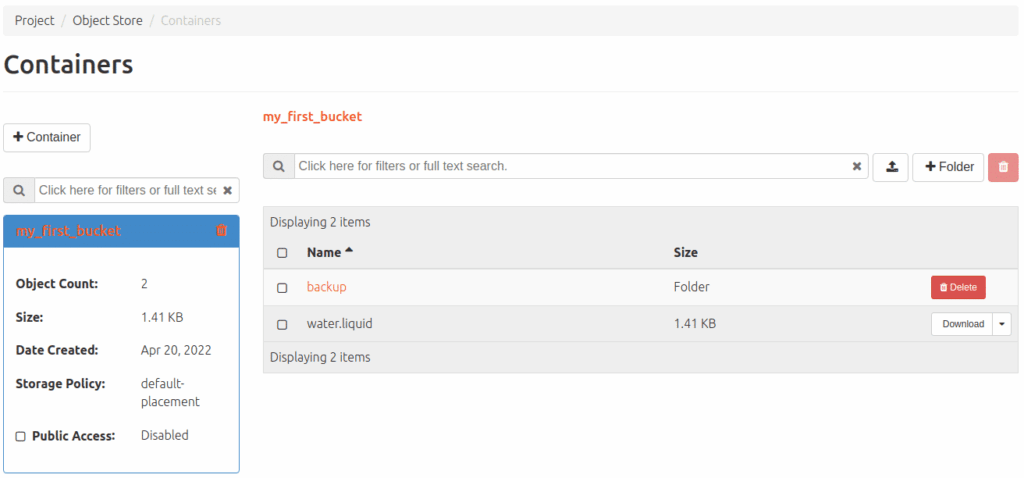
Of course, there are many more parameters for the s3cmd, all of which can be listed using -help. When using s3, however, modern and elegant procedures can also be integrated, e.g. the lifetime of a file with a predefined deletion date. In the cloud, you can also see what the object storage is doing by navigating to the corresponding menu via Project>Object storage.
Incidentally, our object storage also works with swift – so it is also addressed by the cloud itself. So a mixed operation of S3 and swift is possible at will. We have not yet documented swift any further, but our friendly MyEngineer® will be happy to provide information on request. The prices for our Objectstorage and everything else we offer at NWS can be found here at any time.





0 Comments